SiFive 博客
来自 RISC-V 专家的最新洞察与深度技术解析

Part 1: Fast Access to Accelerators: Enabling Optimized Data Transfer with RISC-V
This is the first in a series of blogs about Domain-specific accelerators (DSAs), which are becoming increasingly common in systems-on-chip (SoCs). A DSA provides higher performance per watt than a general-purpose processor by optimizing the specialized function it implements. Examples of DSAs include compression/decompression units, random number generators and network packet processors. A DSA is typically connected to the core complex using a standard IO interconnect, such as an AXI bus.
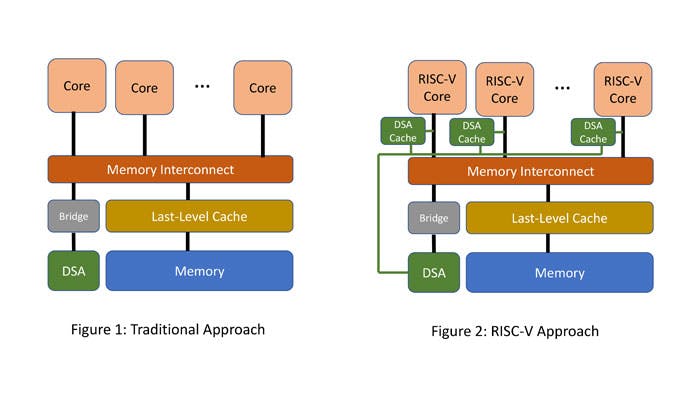
Unfortunately, data transfers between DSAs and the core complex, which are often critical, can be inefficient in traditional SoCs. Figure 1 shows that the datapath between a DSA and core complex in a traditional SoC traverses multiple interconnects and bridges. This increases the latency between the cores and a DSA to 100s of cycles. Consequently, this makes it difficult to have fine-grain interaction between cores and a DSA.
RISC-V offers a unique opportunity to optimize such fine-grain communication between cores and DSAs. For example, as Figure 2 shows, a DSA can export a per-core DSA cache sitting next to a RISC-V core. The RISC-V core can poll status changes out of the DSA cache, thereby reducing the latency of interaction between the core and DSA to tens of cycles. The DSA can update status changes in the DSA cache through a sideband network. Others [1, 2] have argued for similar mechanisms.
The DSA cache can further improve core-DSA interaction performance by prefetching data from the DSA and merging small IO writes into bigger chunks. A RISC-V core could even integrate some of these mechanisms within the core pipeline, if one were to design a custom RISC-V core.
[1] J. Mcalpin, "Notes on Cached Access to Memory-Mapped IO Regions", https://sites.utexas.edu/jdm4372/2013/05/29/notes-on-cached-access-to-memory-mapped-io-regions
[2] Mukherjee, et al., "Coherent Network Interfaces for Fine-Grain Communication," Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, May 1996.
See more details about SiFive’s standard cores, or to customize and build domain-specific RISC-V cores, please visit sifive.com/risc-v-core-ip