SiFive 博客
来自 RISC-V 专家的最新洞察与深度技术解析

Part 2: High-Bandwidth Core Access to Accelerators: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V
This is the second in a series of blogs about Domain-specific accelerators (DSAs), which are becoming increasingly common in SoCs. Part #1 addressed the challenges associated with data transfers between DSAs and the core complex, and showed how RISC-V offers a unique opportunity to optimize fine-grain communication between them and improve core-DSA interaction performance.
To recap, a DSA provides higher performance per watt by optimizing the specialized function it implements. Examples of DSAs include compression/decompression units, random number generators and network packet processors. A DSA is typically connected to the core complex using a standard IO interconnect, such as an AXI bus (Figure 1).
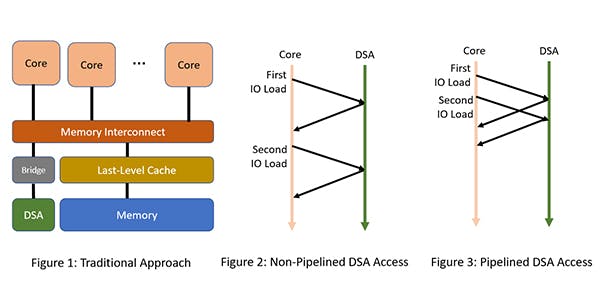
RISC-V offers a unique opportunity to optimize high-bandwidth communication between cores and DSAs. Cores often issue fine-grain load and store instructions in the IO space to access DSA memory. The problem, however, is that these loads and stores to DSA memory might have side effects. For example, a load to a specific DSA memory address might trigger a network message as a side effect of the load. Typically, because of such side effects, loads and stores from a core to an IO device are required to be observed by the IO device in order. This is also known as point-to-point ordering.
A naive way to implement such point-to-point ordering is to issue a load to a DSA and wait for the result to return to the core (Figure 2). This is highly inefficient because successive loads or stores to DSA memory cannot be issued back-to-back in a pipelined fashion. A RISC-V implementation would typically implement such IO loads in a pipelined fashion with help from the interconnect between the core and DSA (Figure 3). For example, if a mesh topology uses a fixed path (e.g., X-Y routing) from the core to the DSA (perhaps via the IO bridge), then the interconnect can guarantee the ordering and thereby allow very high bandwidth access to DSA memory
The RISC-V architecture itself offers two other modes of optional IO ordering. First, RISC-V offers a very conservative IO ordering mode, which can be selectively used to guarantee strong ordering when necessary. Second, RISC-V offers a high-bandwidth relaxed ordering mode where IO loads and stores can be reordered. This mode would typically be used for DSA memory that does not have side effects.
See more details about SiFive’s standard cores, or to customize and build domain-specific RISC-V cores, please visit sifive.com/risc-v-core-ip
Read the other posts in this series:
- Part 1: High-Bandwidth Accelerator Access to Memory: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V
- Part 2: High-Bandwidth Core Access to Accelerators: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V
- Part 3: High-Bandwidth Accelerator Access to Memory: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V