SiFive 博客
来自 RISC-V 专家的最新洞察与深度技术解析

Part 4: High-Performance Interconnect for Accelerators: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V
This is the fourth in a series of blogs about Domain-specific accelerators (DSAs), which are becoming increasingly common in systems-on-chip (SoCs). Parts 1, 2 and 3 addressed key challenges such as data transfers between DSAs and the core complex, point-to-point ordering between cores and DSA memory, and data transfers between DSA and memories. This fourth instalment in the series will focus on the frequent interaction with and amongst cores, which is required by DSAs, and how the TileLink specification can be utilized to build interconnection networks.
To recap, a DSA provides higher performance per watt by optimizing the specialized function it implements. Examples of DSAs include compression/decompression units, random number generators and network packet processors. A DSA is typically connected to the core complex using a standard IO interconnect, such as an AXI bus (Figure 1).
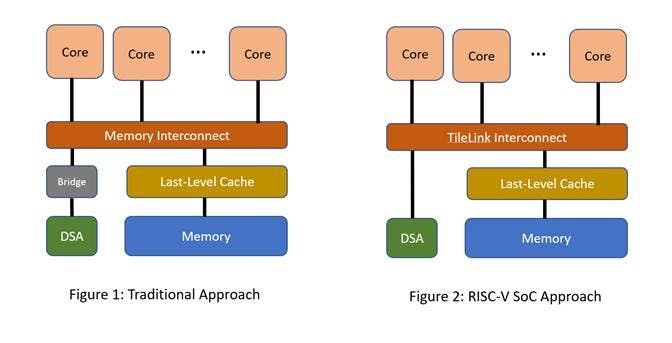
SOCs based on RISC-V offer a unique opportunity to optimize data transfers between cores and DSAs. Many high-performance DSAs require frequent interaction with and amongst cores. Standard memory interconnects often are limited by how fast they can transfer data. Such an interconnection can be designed to the TileLink specification [1], which is a free and open standard to build interconnection networks.
Designing one’s own memory interconnection network offers several advantages to a DSA (Figure 2):
- The DSA can connect to the memory interconnect to reduce latency of interaction with cores by directly participating in the memory coherence protocol.
- The interconnect channel width can be optimized to the data transfer rates required by the DSA. For example, one could envision extremely wide 1024-bit wide channels. The interconnection channels can also be run at a higher frequency than what a standard interconnect might allow.
- The Last-Level Cache (LLC) can have bigger cache block sizes than the core caches. For example, core caches typically have 64-byte blocks, whereas the LLC could be designed for 128-byte or 256-byte cache blocks. The LLC can also support special prefetch mechanisms optimized for the DSA.
- The LLC and interconnect can offer different levels of QoS (Quality of Service). These QoS levels can be used, for example, by the LLC controller, to offer lower latency and higher bandwidth to DSAs in the presence of cross-traffic from different applications.
[1] SiFive TileLink Specification, tilelink spec 1.8.1 PDF
See more details about SiFive’s standard cores, or to customize and build domain-specific RISC-V cores, please visit sifive.com/risc-v-core-ip